Global branding is when products or services are marketed under the same name in various different countries. These products have similar marketing strategies with their advertising, positioning, personality, and look and feel remaining mostly unchanged from one country to another.
 According to an article by Small Business, “global branding means using standardized global advertising and global marketing strategies. It’s basically a method of designing standardized global advertising and global marketing strategies in order to develop a product or service that is recognized worldwide, regardless of the country, continent or region where it is marketed.” Global brands are recognized everywhere. By using similar marketing strategies to promote the brand all over, companies make sure that the brand is being presented reliably in every market.
According to an article by Small Business, “global branding means using standardized global advertising and global marketing strategies. It’s basically a method of designing standardized global advertising and global marketing strategies in order to develop a product or service that is recognized worldwide, regardless of the country, continent or region where it is marketed.” Global brands are recognized everywhere. By using similar marketing strategies to promote the brand all over, companies make sure that the brand is being presented reliably in every market.
One of the great things about global branding Is how companies benefit through the economies of scale. This means that although languages and customs may differ, brands can use the same advertising strategy, brand images and brand representations anywhere. For example, McDonald’s, Google, Disney, and Apple are some brands who remain unchanged regardless of what country they are being marketed in. Each of these companies have had tremendous success in using the same marketing strategies and images to advertise their product regardless of where they are in the world. This has become easier to do in our modern age due to the internet.
 Global branding has various benefits for consumers. The first advantage is that because the brand is globally known, products are very easily identified so consumers tend to be quicker to purchase. Consumers also tend to believe that globally marketed brands are of better quality since they are sold everywhere. This means that the brand has a strong presence regardless of country, language, tradition, and beliefs. The product breaks all barriers, which is difficult to do. Another benefit is that prices tend to be consistent. This means that an Apple iPhone will charge you roughly the same amount in the United States as it will in Italy.
Global branding has various benefits for consumers. The first advantage is that because the brand is globally known, products are very easily identified so consumers tend to be quicker to purchase. Consumers also tend to believe that globally marketed brands are of better quality since they are sold everywhere. This means that the brand has a strong presence regardless of country, language, tradition, and beliefs. The product breaks all barriers, which is difficult to do. Another benefit is that prices tend to be consistent. This means that an Apple iPhone will charge you roughly the same amount in the United States as it will in Italy.
Due to their quality and consistency, globally marketed brands draw in consumer loyalty because they are often seen as dependable and consistent. This means that these companies can charge a premium for  their products since consumers are willing to pay more for something that they believe they are getting their money’s worth for. It makes sense for companies that are doing well and leaving a large footprint to expand globally and then adapt their brand to the country’s culture for optimal success. This allows the product to really understand the customer and merge with their values and traditions while still maintaining the same quality and consistency being offered everywhere else.
their products since consumers are willing to pay more for something that they believe they are getting their money’s worth for. It makes sense for companies that are doing well and leaving a large footprint to expand globally and then adapt their brand to the country’s culture for optimal success. This allows the product to really understand the customer and merge with their values and traditions while still maintaining the same quality and consistency being offered everywhere else.
An article by the Harvard Business Review makes a valid point. “All multinational companies should actively engage in global brand management. Any company that tries to get by with unconnected and directionless local brand strategies will inevitably find mediocrity as its reward.”
 Actionable insights are actions which are direct and meaningful that are taken when raw data is analyzed. However, not all insights are considered actionable. An insight becomes actionable when information is analyzed, and conclusions can be drawn, and decisions made. This means that when actionable insights are available, strategic and well-thought-out decisions can be made, allowing these insights to drive business growth and other positive results from insights that were acquired directly from customers.
Actionable insights are actions which are direct and meaningful that are taken when raw data is analyzed. However, not all insights are considered actionable. An insight becomes actionable when information is analyzed, and conclusions can be drawn, and decisions made. This means that when actionable insights are available, strategic and well-thought-out decisions can be made, allowing these insights to drive business growth and other positive results from insights that were acquired directly from customers. Once the sorted and visualized data has been delivered to a team, it can be reviewed to see if there are commonalities in the data. Understanding a customer’s needs it essential to the livelihood of a business. When companies begin using large analytics and visualizations platforms and bringing analytics strategies and business objectives together, companies really begin reaping benefits from actionable data.
Once the sorted and visualized data has been delivered to a team, it can be reviewed to see if there are commonalities in the data. Understanding a customer’s needs it essential to the livelihood of a business. When companies begin using large analytics and visualizations platforms and bringing analytics strategies and business objectives together, companies really begin reaping benefits from actionable data.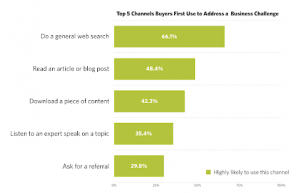 When a company has the right data and tools, brands can be measured quickly. For example, for those popular brands with large social followings, companies can track their brands in real-time by using social listening tools which measure who is mentioning their brand, whether it be positive or negative. One of the reasons brand tracking is so important is because by creating brand messages that consumers can relate to emotionally, their loyalty increases, and churn rates reduce. Also, thanks to brand tracking, when a company knows they have a strong brand, they can begin to charge higher brand premiums.
When a company has the right data and tools, brands can be measured quickly. For example, for those popular brands with large social followings, companies can track their brands in real-time by using social listening tools which measure who is mentioning their brand, whether it be positive or negative. One of the reasons brand tracking is so important is because by creating brand messages that consumers can relate to emotionally, their loyalty increases, and churn rates reduce. Also, thanks to brand tracking, when a company knows they have a strong brand, they can begin to charge higher brand premiums.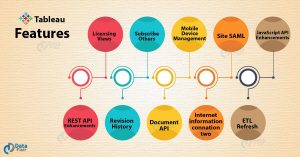 other words, visual analytics makes complex information much easier to understand so that businesses can access data and make decisions quickly. This means businesses can efficiently solve relevant issues like never before.
other words, visual analytics makes complex information much easier to understand so that businesses can access data and make decisions quickly. This means businesses can efficiently solve relevant issues like never before. work with all types of unordered data and create many varieties of visualizations. Another strong feature is the platform’s ability to work with data regardless of what source it comes from. The tool allows users to connect many different data sources and blend them to create resourceful visualizations. Not to mention, adding data sets is made incredibly easy by using common fields.
work with all types of unordered data and create many varieties of visualizations. Another strong feature is the platform’s ability to work with data regardless of what source it comes from. The tool allows users to connect many different data sources and blend them to create resourceful visualizations. Not to mention, adding data sets is made incredibly easy by using common fields. Have you ever been on a company’s website and read the About page? Typically, the company’s story is found here. This is where they explain to consumers who they are and what their brand is about. Oftentimes, the company’s mission is evident through their messages and marketing materials as well. The other part of the brand story lies within the brand’s consumers. It is the brand’s job to discover what their stories are and how a brand can help them reach the solution to whatever problem it is they may have. Finally, storytelling is used in branding to tell marketing stories. In order for a company to best connect with their customers on an emotional level, storytelling is used. When consumers are convinced that they need a product or service, storytelling helps them connect with the brand. Marketing techniques oftentimes won’t reach consumer in the same way that storytelling would, making it a crucial part of marketing.
Have you ever been on a company’s website and read the About page? Typically, the company’s story is found here. This is where they explain to consumers who they are and what their brand is about. Oftentimes, the company’s mission is evident through their messages and marketing materials as well. The other part of the brand story lies within the brand’s consumers. It is the brand’s job to discover what their stories are and how a brand can help them reach the solution to whatever problem it is they may have. Finally, storytelling is used in branding to tell marketing stories. In order for a company to best connect with their customers on an emotional level, storytelling is used. When consumers are convinced that they need a product or service, storytelling helps them connect with the brand. Marketing techniques oftentimes won’t reach consumer in the same way that storytelling would, making it a crucial part of marketing. As an article by
As an article by 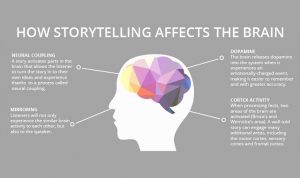
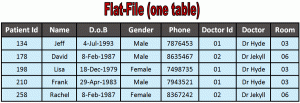 Flat file databases have similar functionalities but adding a new field is required whenever new data is to be added. For example, think of a cosmetics company that is interested in tracking what cosmetic products their clients order so that they can best devise marketing messages for this target audience. Let’s say the company wants to know how often their customers are purchasing products from them, where they are purchasing from, how much money they are spending on average, and other important pieces of data. If marketers were to acquire this information from a flat file database, they would be required to add fields each time and for each customer. This is a lot of work, especially when there is a more efficient way of completing this task.
Flat file databases have similar functionalities but adding a new field is required whenever new data is to be added. For example, think of a cosmetics company that is interested in tracking what cosmetic products their clients order so that they can best devise marketing messages for this target audience. Let’s say the company wants to know how often their customers are purchasing products from them, where they are purchasing from, how much money they are spending on average, and other important pieces of data. If marketers were to acquire this information from a flat file database, they would be required to add fields each time and for each customer. This is a lot of work, especially when there is a more efficient way of completing this task.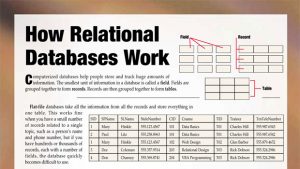 So what does this all mean? Relational databases allow for more organized and efficient email marketing. Different kinds of data can be tacked onto customers meaning that these databases can segment in a way that flat file databases can’t. When customers are segmented, marketing emails can be personalized for each consumer segment and can bring more conversions for the business. Think about it. If you receive a personalized email that targets your specific needs and buyer preferences, you
So what does this all mean? Relational databases allow for more organized and efficient email marketing. Different kinds of data can be tacked onto customers meaning that these databases can segment in a way that flat file databases can’t. When customers are segmented, marketing emails can be personalized for each consumer segment and can bring more conversions for the business. Think about it. If you receive a personalized email that targets your specific needs and buyer preferences, you  may be more inclined to click rather than if you had received a. general email about products that you aren’t interested in.
may be more inclined to click rather than if you had received a. general email about products that you aren’t interested in. While many marketers would argue that neuromarketing us a helpful field that can assist with the information needed to better create services and products that consumers are more interested in purchasing, many people would argue that it is an unethical practice. Neuromarketing falls under subliminal advertising, which has long had the reputation of manipulating the consumer’s mind. According to an article by
While many marketers would argue that neuromarketing us a helpful field that can assist with the information needed to better create services and products that consumers are more interested in purchasing, many people would argue that it is an unethical practice. Neuromarketing falls under subliminal advertising, which has long had the reputation of manipulating the consumer’s mind. According to an article by 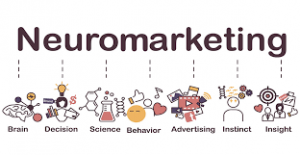
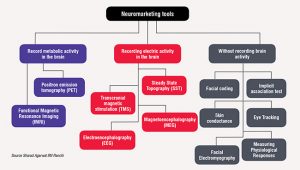 While there are certainly a variety of ethical and unethical cases in which neuromarketing has been utilized, such as health campaigns, political campaigns, and for charity organizations, it is important for companies to maintain their reputation by instilling trust in their consumers. Consumers do not want to feel threatened or like their privacy has been violated. However, when a company has built trust in the mind of the consumer, it becomes easier for them to use neuromarketing. In the end, the field of neuromarketing is not necessarily what is unethical, but what companies decide to do with the information provided can be. Neuromarketing has both advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important for marketers to use this field of marketing responsibly and for consumers to be aware of the practice.
While there are certainly a variety of ethical and unethical cases in which neuromarketing has been utilized, such as health campaigns, political campaigns, and for charity organizations, it is important for companies to maintain their reputation by instilling trust in their consumers. Consumers do not want to feel threatened or like their privacy has been violated. However, when a company has built trust in the mind of the consumer, it becomes easier for them to use neuromarketing. In the end, the field of neuromarketing is not necessarily what is unethical, but what companies decide to do with the information provided can be. Neuromarketing has both advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important for marketers to use this field of marketing responsibly and for consumers to be aware of the practice. By dissecting data collection and how it is organized, marketers can better understand how to approach these needs. Understanding the
By dissecting data collection and how it is organized, marketers can better understand how to approach these needs. Understanding the 

 value, in turn allowing them to charge a premium. As a result, their customers tend to not only be loyal but also buy a variety of products and services from the brand because they trust it. These kinds of companies deliver sustained earnings and possibilities for future growth, so they are able to have higher market values and lower costs of capital. This is an exceptional position for a brand to be in.
value, in turn allowing them to charge a premium. As a result, their customers tend to not only be loyal but also buy a variety of products and services from the brand because they trust it. These kinds of companies deliver sustained earnings and possibilities for future growth, so they are able to have higher market values and lower costs of capital. This is an exceptional position for a brand to be in. One such company is The Weinstein Company. Although it was once one of the strongest American independent film companies, the sexual abuse accusations that Harvey Weinstein has been engulfed in the past few years has sent the brand on a downward spiral. According to an article by
One such company is The Weinstein Company. Although it was once one of the strongest American independent film companies, the sexual abuse accusations that Harvey Weinstein has been engulfed in the past few years has sent the brand on a downward spiral. According to an article by  Another major brand which has run into many problems recently is Uber. Although Uber gained a global reputation as a luxurious convenience by trademarking itself as “everyone’s private driver,” a lot has changed recently. Between facing various lawsuits in 2017 for sexual harassment, allegedly interfering with rival company Lyft, and the alleged theft of intellectual property, the Uber brand is not currently in good shape. According to
Another major brand which has run into many problems recently is Uber. Although Uber gained a global reputation as a luxurious convenience by trademarking itself as “everyone’s private driver,” a lot has changed recently. Between facing various lawsuits in 2017 for sexual harassment, allegedly interfering with rival company Lyft, and the alleged theft of intellectual property, the Uber brand is not currently in good shape. According to  Similar to Uber and The Weinstein Company, United Airlines has received bad press over the years. After videos surfaced of passengers being forcibly removed from their seats, outrage sparked across the U.S. The company’s stock dropped, and their market value went down. According to
Similar to Uber and The Weinstein Company, United Airlines has received bad press over the years. After videos surfaced of passengers being forcibly removed from their seats, outrage sparked across the U.S. The company’s stock dropped, and their market value went down. According to 
 After attaining these calculations, brands can decide whether they want to spend more or less marketing dollars compared to what the market’s BDI is. More of the marketing budget can be spent on areas where the BDI is higher because more of a target audience can then be reached. BDI also tends to be used in conjunction with CDI or category development index. The CDI measures how strong sales are for certain product categories in specific markets and then compares it to the average performance of consumers everywhere. The formula used here is: CDI= [Category sales to group / Households in group] / [Total category sales / Total households]. The outcome allows marketers to pinpoint where the strong and weak segments are located for different service categories. Like the BDI, the CDI contributes by giving marketers important information so that they can better assign advertisements and disburse marketing budgets to certain areas.
After attaining these calculations, brands can decide whether they want to spend more or less marketing dollars compared to what the market’s BDI is. More of the marketing budget can be spent on areas where the BDI is higher because more of a target audience can then be reached. BDI also tends to be used in conjunction with CDI or category development index. The CDI measures how strong sales are for certain product categories in specific markets and then compares it to the average performance of consumers everywhere. The formula used here is: CDI= [Category sales to group / Households in group] / [Total category sales / Total households]. The outcome allows marketers to pinpoint where the strong and weak segments are located for different service categories. Like the BDI, the CDI contributes by giving marketers important information so that they can better assign advertisements and disburse marketing budgets to certain areas.